Table Of Content
- Partisan role
- Speaker of the House, the Role, Duties, and Powers
- officers shot during standoff in Louisiana
- Suspect killed after 3 police officers wounded by gunfire in standoff near New Orleans
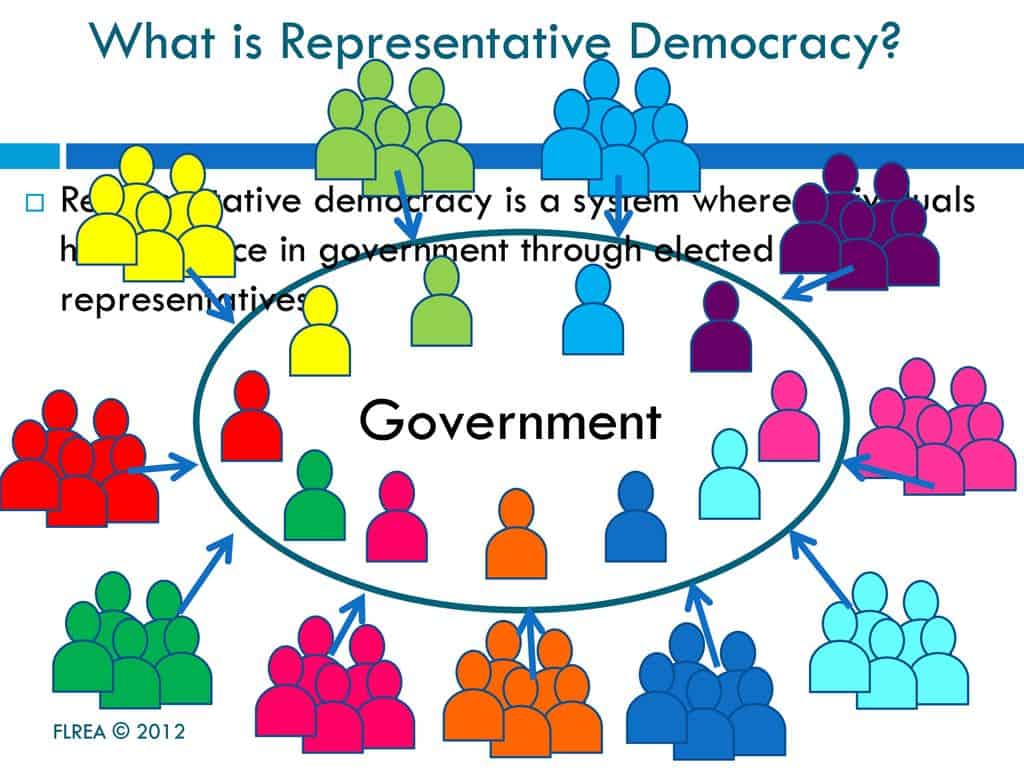
- Speaker of the United States House of Representatives
- Rep. Mike Johnson
- Demonstrations roil US campuses ahead of graduations as protesters spar over the war in Gaza
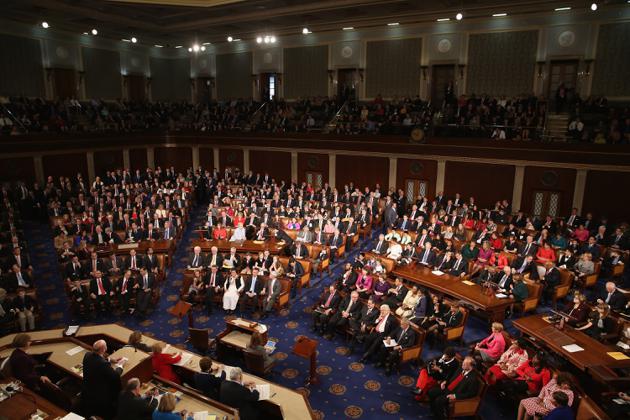

The power of the speaker was greatly augmented during the tenure of the Republican Thomas Brackett Reed (1889–1891, 1895–1899). Reed, however, declared that members who were in the chamber but refused to vote would still count for the purposes of determining a quorum. Through these and other rulings, Reed ensured that the Democrats could not block the Republican agenda. The longest-serving and perhaps most influential Speaker in history was Texas Democrat Sam Rayburn, who served as Speaker from 1940 to 1947, 1949 to 1953, and 1955 to 1961. Working closely with House committees and members from both parties, Speaker Rayburn ensured the passage of several controversial domestic policies and foreign aid bills backed by Presidents Franklin Roosevelt and Harry Truman.
Partisan role
He vigorously used his powers to ensure that Republican proposals were passed by the House. Toward the end of the 19th century, the office of speaker began to develop into a very powerful one. At the time, one of the most important sources of the speaker's power was his position as Chairman of the Committee on Rules, which, after the reorganization of the committee system in 1880, became one of the most powerful standing committees of the House. Furthermore, several speakers became leading figures in their political parties; examples include Democrats Samuel J. Randall, John Griffin Carlisle, and Charles F. Crisp, and Republicans James G. Blaine, Thomas Brackett Reed, and Joseph Gurney Cannon. In 1811, Henry Clay became the first dynamic national political figure to assume the role of Speaker of the House. Since Clay’s three terms in the House, various Speakers have used different leadership styles in their critical jobs as national party spokesperson and House institutional leader.

Speaker of the House, the Role, Duties, and Powers
Typically the head of the majority party in the House, the Speaker outranks the Majority Leader. The salary of the Speaker is also higher than that of the Majority and Minority Leaders in both the House and Senate. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed. (NewsNation) — The House of Representatives remains at a standstill while it is without a speaker, a vacancy that has highlighted the position as one of the most important in Washington.
officers shot during standoff in Louisiana
On two other occasions, lawmakers considered a motion to vacate, but the vote never made it to the House floor. The House is set to reconvene Tuesday, when lawmakers will try to elect a new speaker. The last time, it took 15 rounds of voting for McCarthy to win the position. “Clay championed national policies over regional ones, and he effectively coupled the institutional tools of the speakership with his personal charisma, raising the stature of the House,” the House historian’s office notes. Today, the role of the speaker is influenced especially by changes instituted by Speaker Newt Gingrich, who took the gavel after the 1994 elections.
Today, the Speaker of the House serves in several major constitutional roles. The Speaker is the majority political party leader in the House, which on its own is one of the most powerful jobs in Washington. In addition, the Speaker controls the order of all institutional business on the House floor. The Speaker also votes on business as needed as a representative from a Congressional district. The first politically powerful Speaker, Henry Clay of Kentucky, served between 1810 and 1824.
Suspect killed after 3 police officers wounded by gunfire in standoff near New Orleans
Unlike his predecessors, Clay took part in several heated debates and was influential in winning the passage of legislation he supported, such as the declaration of the War of 1812. When none of the candidates in the controversial presidential election of 1824 received an Electoral College vote, majority, leaving the selection of the president up to the House, Speaker Clay supported John Quincy Adams instead of Andrew Jackson, ensuring Adams’ victory. In 1997, several Republican congressional leaders tried to force Speaker Newt Gingrich to resign. However, Gingrich refused since that would have required a new election for speaker, which could have led to Democrats along with dissenting Republicans voting for Democrat Dick Gephardt (then minority leader) as speaker.
Speaker of the United States House of Representatives
Since Clay’s time, the role of Speaker of the House has become more complex as the size of government has grown. The Speaker is usually selected during party meetings before a new Congress meets, and the House confirms the selection by individual voice votes. Until January 2023, there had not been a Speaker election contested on the House floor since 1923. And the removal of Rep. Kevin McCarthy (R-Calif.) as Speaker of the House is unprecedented in Congressional history. First, they are the most visible and authoritative spokesperson for the majority party in the House.
John Boehner was elected speaker when the 112th Congress convened on January 5, 2011, and was subsequently re-elected twice, at the start of the 113th and 114th Congresses. Since the first organized political parties—the Federalist Party and the Democratic-Republican Party—did not appear until the 1790s, some scholars suggest that early Speakers of the House served largely ceremonial, rather than actively partisan political roles as they do today. The speaker is also third in line to the presidency (after the vice president) and plays a role in the 25th Amendment process of dealing with a presidential incapacitation. The Republicans came out of the 2000 elections with a further reduced majority but made small gains in 2002 and 2004. One of the most influential speakers in history was Democrat Sam Rayburn.[48] Rayburn had the most cumulative time as speaker in history, holding office from 1940 to 1947, 1949 to 1953, and 1955 to 1961. He helped shape many bills, working quietly in the background with House committees.
House Republicans fail to pass short-term funding bill as shutdown deadline looms - ABC News
House Republicans fail to pass short-term funding bill as shutdown deadline looms.
Posted: Fri, 29 Sep 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Two rival delegations, one Whig and the other Democrat, had been certified as elected by different branches of the New Jersey government. The problem was compounded by the fact that the result of the dispute would determine whether the Whigs or the Democrats held the majority. Neither party agreed to permit a speakership election with the opposite party's delegation participating.
When the House resolves itself into a Committee of the Whole, the speaker designates a member to preside over the committee, who is addressed as "Mister Chairman" or "Madam Chairwoman". The presiding officer also rules on all points of order but such rulings may be appealed to the whole House. The speaker is responsible for maintaining decorum in the House and may order the Sergeant-at-Arms to enforce House rules. On the other hand, when the speaker and the president belong to opposite parties, the public role and influence of the speaker tend to increase. As the highest-ranking member of the opposition party (and de facto leader of the opposition), the speaker is normally the chief public opponent of the president's agenda. In this scenario, the speaker is known for undercutting the president's agenda by blocking measures by the minority party or rejecting bills by the Senate.
Elected Speaker on April 1, 1789, the day the House convened to start the 1st session of the 1st U.S. Congress, Muhlenberg went on to serve two non-consecutive terms as Speaker, from 1789 to 1791 in the 1st Congress and from 1793 to 1795 in the 3rd Congress. That last duty is why, until a new speaker is elected, Congress will be unable to take action on important end-of-year items, including passing a federal budget. While legislators were able to reach a deal on a temporary funding measure — the reason behind former Speaker Kevin McCarthy’s ouster — they must pass another before Nov. 17. Katherine ClarkAssists leadership in managing party's legislative program.
The roles of the parties reversed in 1994 when, after spending forty years in the minority, the Republicans regained control of the House with the "Contract with America", an idea spearheaded by Minority Whip Newt Gingrich. Speaker Gingrich would regularly clash with Democratic President Bill Clinton, leading to the United States federal government shutdown of 1995 and 1996, in which Clinton was largely seen to have prevailed. Gingrich's hold on the leadership was weakened significantly by that and several other controversies, and he faced a caucus revolt in 1997.

No comments:
Post a Comment